| farads | microfarads | nanofarads | picofarads | abfarads | statfarads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 F | 1,000,000 μF | 1,000,000,000 nF | 1,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000001 abF | 898,755,224,015 stF |
| 2 F | 2,000,000 μF | 2,000,000,000 nF | 2,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000002 abF | 1,797,510,448,030 stF |
| 3 F | 3,000,000 μF | 3,000,000,000 nF | 3,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000003 abF | 2,696,265,672,044 stF |
| 4 F | 4,000,000 μF | 4,000,000,000 nF | 4,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000004 abF | 3,595,020,896,059 stF |
| 5 F | 5,000,000 μF | 5,000,000,000 nF | 5,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000005 abF | 4,493,776,120,074 stF |
| 6 F | 6,000,000 μF | 6,000,000,000 nF | 6,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000006 abF | 5,392,531,344,088 stF |
| 7 F | 7,000,000 μF | 7,000,000,000 nF | 7,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000007 abF | 6,291,286,568,103 stF |
| 8 F | 8,000,000 μF | 8,000,000,000 nF | 8,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000008 abF | 7,190,041,792,118 stF |
| 9 F | 9,000,000 μF | 9,000,000,000 nF | 9,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000009 abF | 8,088,797,016,133 stF |
| 10 F | 10,000,000 μF | 10,000,000,000 nF | 10,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.00000001 abF | 8,987,552,240,147 stF |
| 11 F | 11,000,000 μF | 11,000,000,000 nF | 11,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000011 abF | 9,886,307,464,162 stF |
| 12 F | 12,000,000 μF | 12,000,000,000 nF | 12,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000012 abF | 10,785,062,688,177 stF |
| 13 F | 13,000,000 μF | 13,000,000,000 nF | 13,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000013 abF | 11,683,817,912,192 stF |
| 14 F | 14,000,000 μF | 14,000,000,000 nF | 14,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000014 abF | 12,582,573,136,206 stF |
| 15 F | 15,000,000 μF | 15,000,000,000 nF | 15,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000015 abF | 13,481,328,360,221 stF |
| 16 F | 16,000,000 μF | 16,000,000,000 nF | 16,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000016 abF | 14,380,083,584,236 stF |
| 17 F | 17,000,000 μF | 17,000,000,000 nF | 17,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000017 abF | 15,278,838,808,251 stF |
| 18 F | 18,000,000 μF | 18,000,000,000 nF | 18,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000018 abF | 16,177,594,032,265 stF |
| 19 F | 19,000,000 μF | 19,000,000,000 nF | 19,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.000000019 abF | 17,076,349,256,280 stF |
| 20 F | 20,000,000 μF | 20,000,000,000 nF | 20,000,000,000,000 pF | 0.00000002 abF | 17,975,104,480,295 stF |
| Symbol | Component name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Wire Symbols |
||
| Electrical Wire | Conductor of electrical current | |
| Connected Wires | Connected crossing | |
| Not Connected Wires | Wires are not connected | |
Switch Symbols and Relay Symbols |
||
| SPST Toggle Switch | Disconnects current when open | |
| SPDT Toggle Switch | Selects between two connections | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.O) | Momentary switch - normally open | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.C) | Momentary switch - normally closed | |
| DIP Switch | DIP switch is used for onboard configuration | |
| SPST Relay | Relay open / close connection by an electromagnet | |
| SPDT Relay | ||
| Jumper | Close connection by jumper insertion on pins. | |
| Solder Bridge | Solder to close connection | |
Ground Symbols |
||
| Earth Ground | Used for zero potential reference and electrical shock protection. | |
| Chassis Ground | Connected to the chassis of the circuit | |
| Digital / Common Ground | ||
Resistor Symbols |
||
| Resistor (IEEE) | Resistor reduces the current flow. | |
| Resistor (IEC) | ||
| Potentiometer (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 3 terminals. | |
| Potentiometer (IEC) | ||
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 2 terminals. | |
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEC) | ||
| Trimmer Resistor | Preset resistor | |
| Thermistor | Thermal resistor - change resistance when temperature changes | |
| Photoresistor / Light dependent resistor (LDR) | Photo-resistor - change resistance with light intensity change | |
Capacitor Symbols |
||
| Capacitor | Capacitor is used to store electric charge. It acts as short circuit with AC and open circuit with DC. | |
| Capacitor | ||
| Electrolytic capacitor | ||
| Polarized Capacitor | Electrolytic capacitor | |
| Variable Capacitor | Adjustable capacitance | |
Inductor / Coil Symbols |
||
| Inductor | Coil / solenoid that generates magnetic field | |
| ">Iron Core Inductor | Includes iron | |
| ">Variable Inductor | ||
Power Supply Symbols |
||
| Voltage Source | Generates constant voltage | |
| Current Source | Generates constant current. | |
| AC Voltage Source | AC voltage source | |
| Generator | Electrical voltage is generated by mechanical rotation of the generator | |
| Battery Cell | Generates constant voltage | |
| Battery | Generates constant voltage | |
| Controlled Voltage Source | Generates voltage as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
| Controlled Current Source | Generates current as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
Meter Symbols |
||
| Voltmeter | Measures voltage. Has very high resistance. Connected in parallel. | |
| Ammeter | Measures electric current. Has near zero resistance. Connected serially. | |
| Ohmmeter | Measures resistance | |
| Wattmeter | Measures electric power | |
Lamp / Light Bulb Symbols |
||
| Lamp / light bulb | Generates light when current flows through | |
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
Diode / LED Symbols |
||
| Diode | Diode allows current flow in one direction only - left (anode) to right (cathode). | |
| Zener Diode | Allows current flow in one direction, but also can flow in the reverse direction when above breakdown voltage | |
| Schottky Diode | Schottky diode is a diode with low voltage drop | |
| Varactor / Varicap Diode | Variable capacitance diode | |
| Tunnel Diode | ||
| Light Emitting Diode (LED) | LED emits light when current flows through | |
| Photodiode | Photodiode allows current flow when exposed to light | |
Transistor Symbols |
||
| NPN Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when high potential at base (middle) | |
|
|
PNP Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when low potential at base (middle) |
|
|
Darlington Transistor | Made from 2 bipolar transistors. Has total gain of the product of each gain. |
|
|
JFET-N Transistor | N-channel field effect transistor |
|
|
JFET-P Transistor | P-channel field effect transistor |
|
|
NMOS Transistor | N-channel MOSFET transistor |
|
|
PMOS Transistor | P-channel MOSFET transistor |
Misc. Symbols |
||
|
|
Motor | Electric motor |
|
|
Transformer | Change AC voltage from high to low or low to high. |
|
|
Electric bell | Rings when activated |
|
|
Buzzer | Produce buzzing sound |
|
|
Fuse | The fuse disconnects when current above threshold. Used to protect circuit from high currents. |
|
|
Fuse | |
|
|
Bus | Contains several wires. Usually for data / address. |
|
|
Bus | |
|
|
Bus | |
|
|
Optocoupler / Opto-isolator | Optocoupler isolates connection to other board |
|
|
Loudspeaker | Converts electrical signal to sound waves |
|
|
Microphone | Converts sound waves to electrical signal |
| Operational Amplifier | Amplify input signal | |
|
|
Schmitt Trigger | Operates with hysteresis to reduce noise. |
| Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) | Converts analog signal to digital numbers | |
| Digital-to-Analog converter (DAC) | Converts digital numbers to analog signal | |
| Crystal Oscillator | Used to generate precise frequency clock signal | |
Antenna Symbols | ||
| Antenna / aerial | Transmits & receives radio waves | |
| Antenna / aerial | ||
| Dipole Antenna | Two wires simple antenna | |
Logic Gates Symbols |
||
| NOT Gate (Inverter) | Outputs 1 when input is 0 | |
| AND Gate | Outputs 1 when both inputs are 1. | |
| NAND Gate | Outputs 0 when both inputs are 1. (NOT + AND) | |
| OR Gate | Outputs 1 when any input is 1. | |
| NOR Gate | Outputs 0 when any input is 1. (NOT + OR) | |
| XOR Gate | Outputs 1 when inputs are different. (Exclusive OR) | |
| D Flip-Flop | Stores one bit of data | |
| Multiplexer / Mux 2 to 1 | Connects the output to selected input line. | |
| Multiplexer / Mux 4 to 1 | ||
| Demultiplexer / Demux 1 to 4 | Connects selected output to the input line. | |
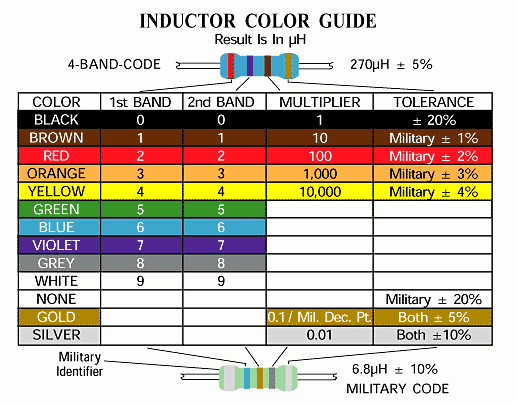
Cylindrical molded choke coils are marked with five colored bands. A wide silver band, located at one end of the coil, identifies military radio-fequency coils. The next three bands indicate the inductance in micro-henries and the fourth band is the tolerance.
Color coding is in accordance with the color code table shown right. If the first or second band is gold, this represents the decimal point for inductance values less than ten. Then the following two bands significant figures. For inductance values of 10 or more, the first two bands represent significant figures and the third is the multiplier.